

So, S, the entropy of the system is a measure of how disordered the system is. Larger the values of S the larger the disorder. The greater is W, the greater is S, more disorder. The fundamental equation of entropy S is S= k ln W, where W is the number of ways of arranging the particles so as to produce a given state, and k is Boltzmann’s constant. The increase in entropy of a system, dS, is given by dS = delta Q/T. The numerator and denominator would both be described as 'number of bits'. Define a compression ratio as (ADC sample size) / (Shannon entropy of sample set). Information theory includes the measurable concept of compression. While the average KE energy of a molecule is the same for all gases and depends only on temperature, The KE per unit mass per unit kelvin is what you measure as specific heat and express it as KJ/kg/k or J/kg/-k. Shannon entropy is normally given 'units' of bits or nats in information theory. So, we can redefine specific heat as a measure of Joule or kinetic energy. The SI unit for the Boltzmann constant is J/k. Heat received by a molecule is equally divided and each mode of motion, called degree of freedom like translation, vibration, and rotation gets ½ KT energy. A molecule can take only that much heat as it can store. This energy per unit mass of the molecule is its specific heat.
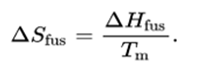
When you heat a molecule let us say a gas molecule, it takes certain energy before its temperature can rise. Standard entropy values (S) are measured under standard conditions of 298K and 100 kPa, with all species in standard states. For example, suppose the transmitter wanted to inform the receiver of the result of a 4-person tournament, where some of the players are better than others. Entropy is a measure of the system's thermal energy unavailable for work per unit temperature.Įntropy is expressed as dS = delta Q/T. The entropy, in this context, is the expected number of bits of information contained in each message, taken over all possibilities for the transmitted message. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K).Įntropy is a measure of the number of ways a system can be arranged, often taken to be a measure of "disorder" (the higher the entropy, the higher the disorder). For standard entropy, this assumes that the. Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The units of entropy are JK-1mol-1, which basically means joules of energy per unit heat (in Kelvin) per mol. In accordance with (1), entropy is measured in cal/ (mole-K) the entropy unitor in J/ (moleK).
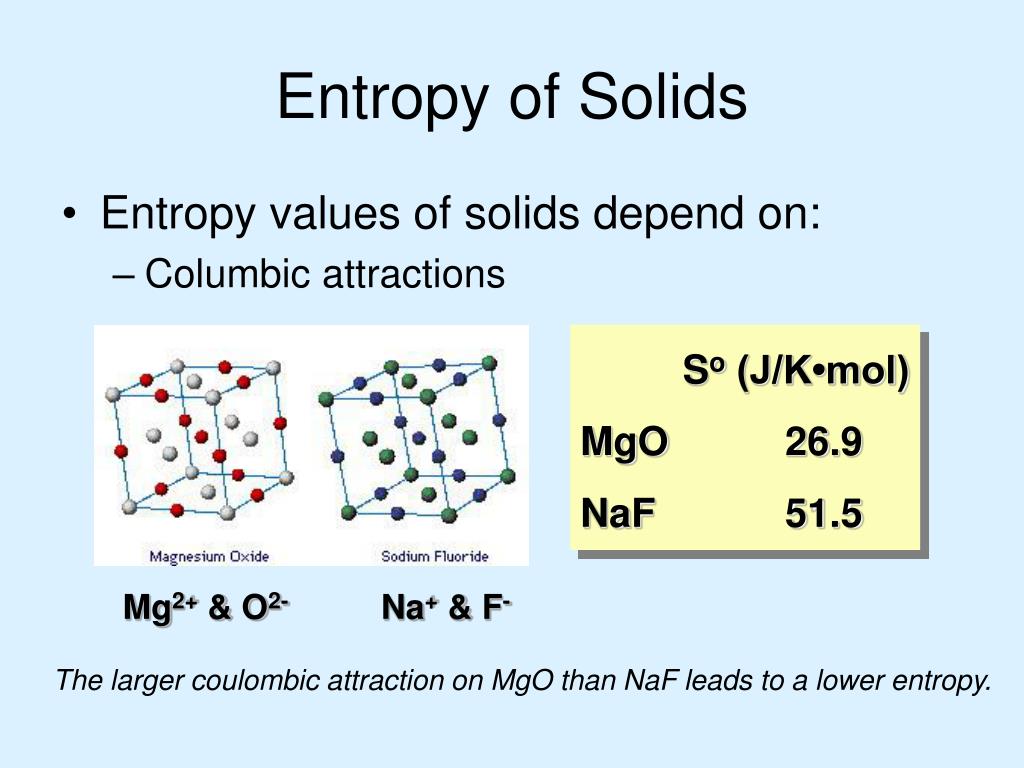
The SI unit of specific heat capacity is joule per kelvin per kilogram, J⋅kg−1⋅K−1 The specific heat capacity (symbol cp) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
